Page 2 - Demo
P. 2
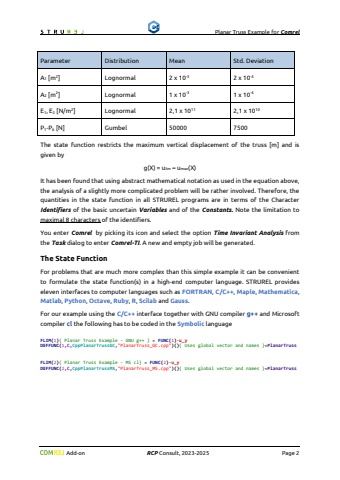
Planar Truss Examplefor ComrelAdd-onRCPConsult, 2023-2025Page 2ParameterDistributionMeanStd. DeviationA1[m2]Lognormal2 x 10-32 x 10-4A2[m2]Lognormal1 x 1031 x 104E1, E2[N/m2]Lognormal2,1 x 10112,1 x 1010P1-P6[N]Gumbel500007500The state function restricts the maximum vertical displacement of the truss [m] and is given byg(X) = ulim%u2013umax(X)It has been found that using abstract mathematical notation as used in the equation above, the analysis of a slightly more complicated problem will be rather involved. Therefore, the quantities in the state function in all STRUREL programs are in terms of the Character Identifiersof the basic uncertain Variablesand of the Constants. Note the limitation to maximal8charactersof the identifiers.You enter Comrelby picking its icon and select the option Time Invariant Analysisfrom the Taskdialog to enter Comrel-TI. A new and empty job will be generated.The State FunctionFor problems that are much more complex than this simple example it can be convenient to formulate the state function(s) in a high-end computer language. STRUREL provides eleveninterfaces to computer languagessuch as FORTRAN, C/C++, Maple, Mathematica, Matlab, Python, Octave,Ruby, R,Scilab and Gauss.For our example using the C/C++interface together with GNU compilerg++andMicrosoft compilerclthe following has to be coded in the SymboliclanguageFLIM(1){ Planar Truss Example -GNU g++ }= FUNC(1)-u_yDEFFUNC(1,C,CppPlanarTrussGC,\_GC.cpp\FLIM(2){ Planar Truss Example -MS cl}= FUNC(2)-u_yDEFFUNC(2,C,CppPlanarTrussMS,\_MS.cpp\